Getting Started with RiBot
What is RiBot?
RiBot is a sophisticated software control system specifically designed for robotic arms. It stands out for its user-friendly nature and its capacity to be effortlessly extended or customized according to the user's needs. Essentially, RiBot acts as the brain of a robotic arm, providing the necessary instructions and controls to execute complex tasks.
What RiBot is Not
It's important to clarify that RiBot itself is not a physical robot arm. Instead, it is a software layer that operates robotic arms. Think of RiBot as the mind that guides and controls the movements and functions of a robot arm, but not the physical machinery itself.
Main Features of RiBot
With RiBot, users gain access to:
-
An Easy-to-Use Web Interface: This intuitive interface allows users to easily control the robotic arm and create movement routines. The focus on simplicity ensures that even those with minimal technical experience can operate the system effectively.
-
A Powerful API: RiBot's API allows users to control the robotic arm using the Python programming language. This feature is ideal for those who want to integrate RiBot with other systems or create custom applications.
-
A Versatile System: RiBot is compatible with a wide range of robotic arms, stepper motors, and stepper motor drivers. This versatility allows users to customize the system according to their needs.
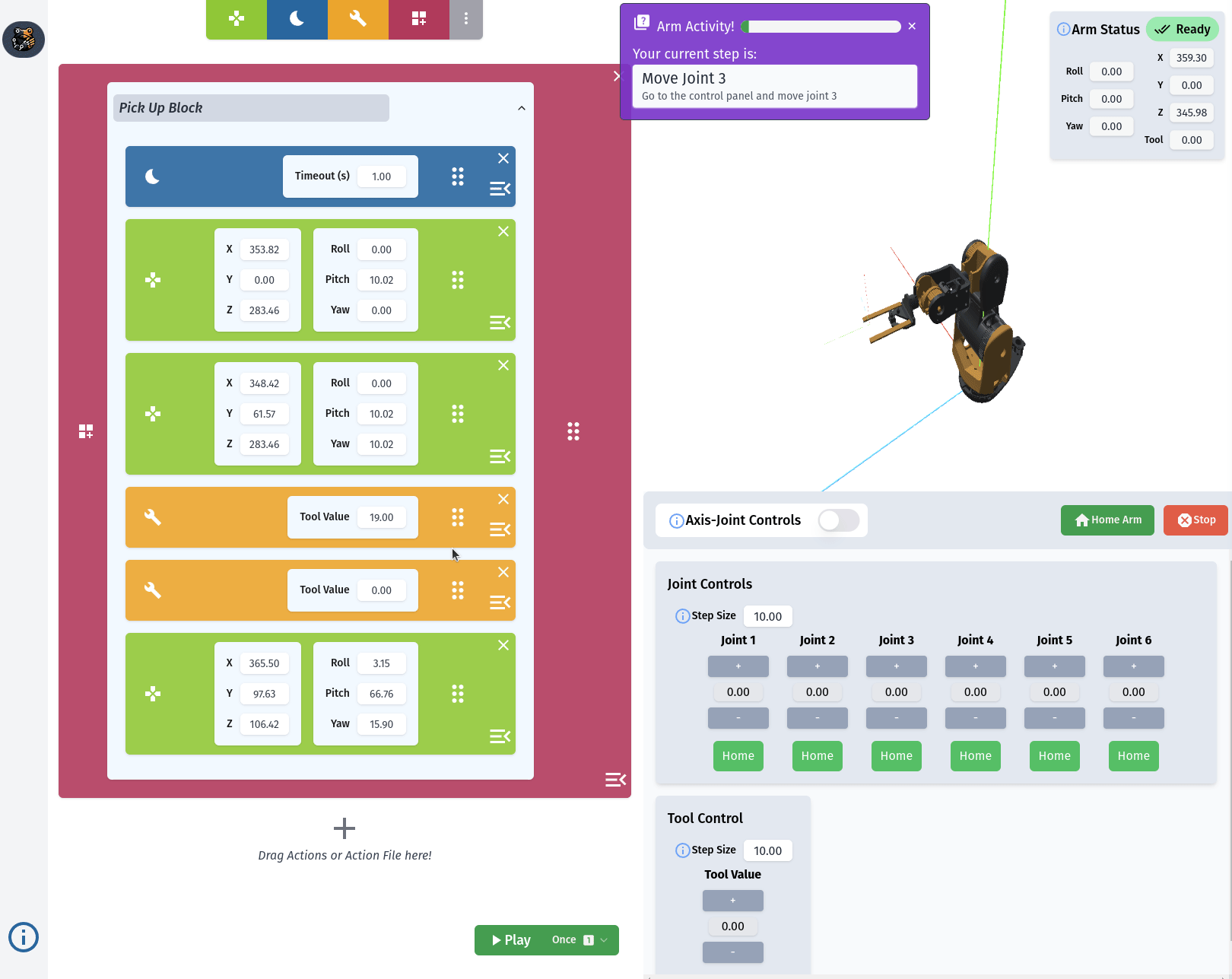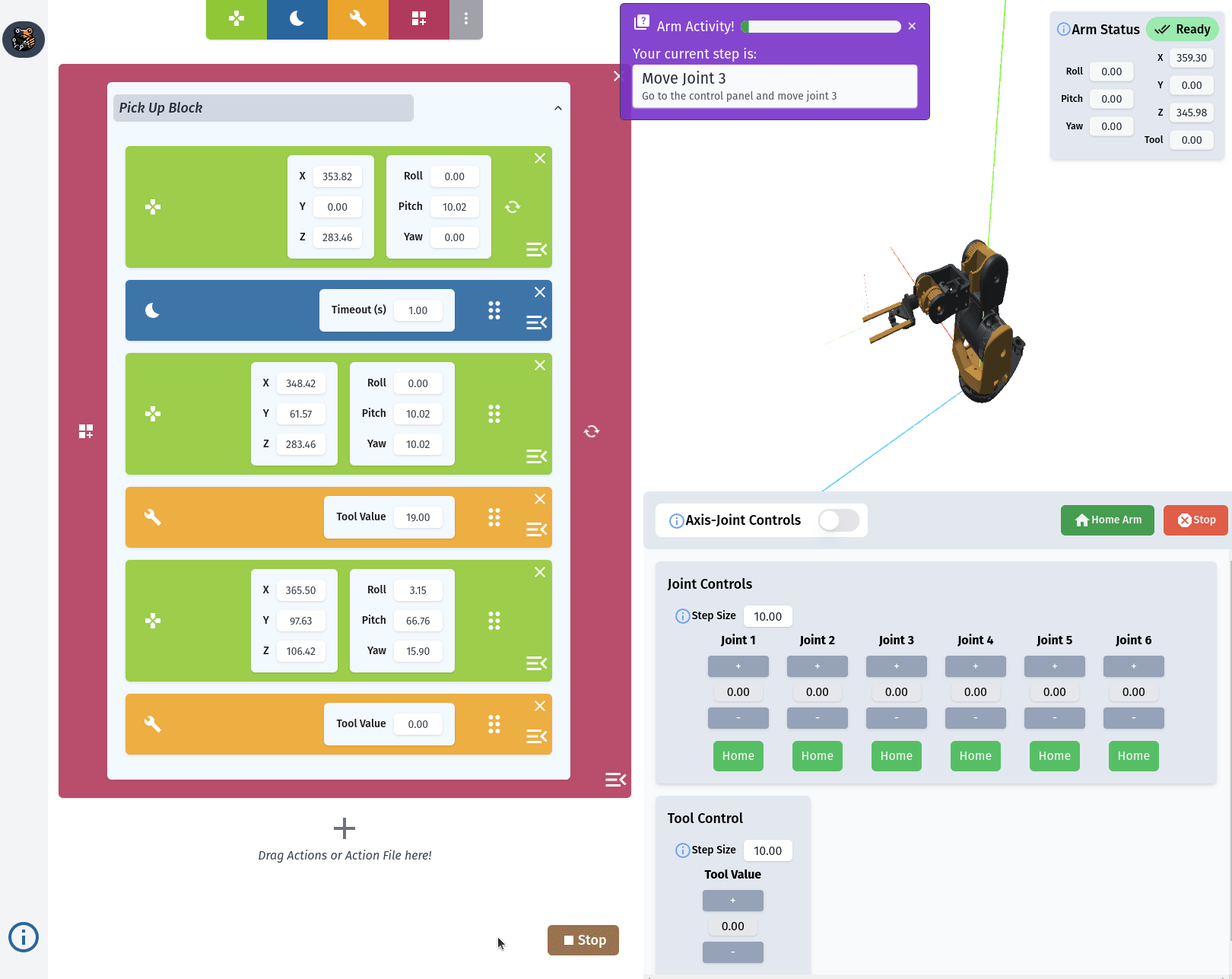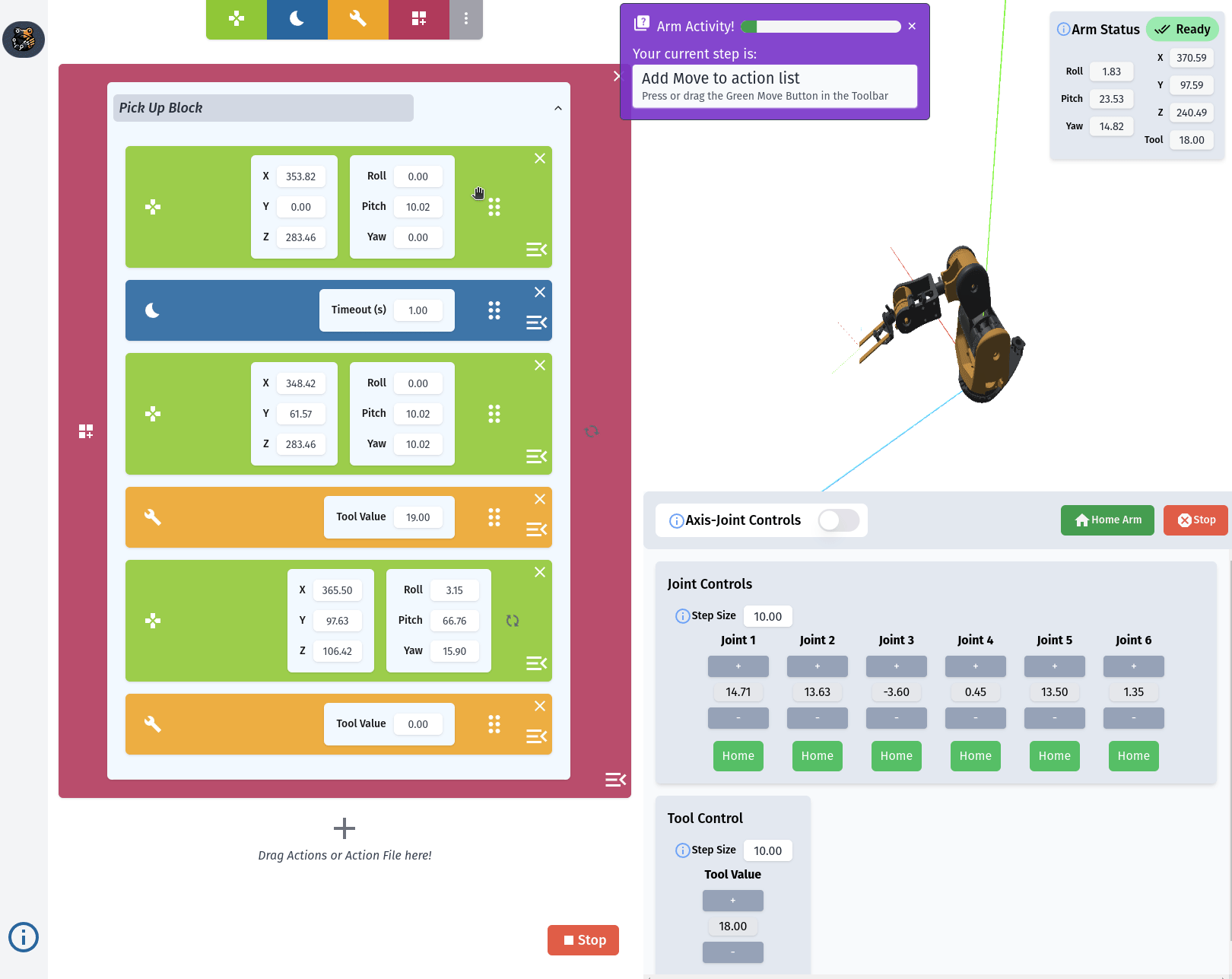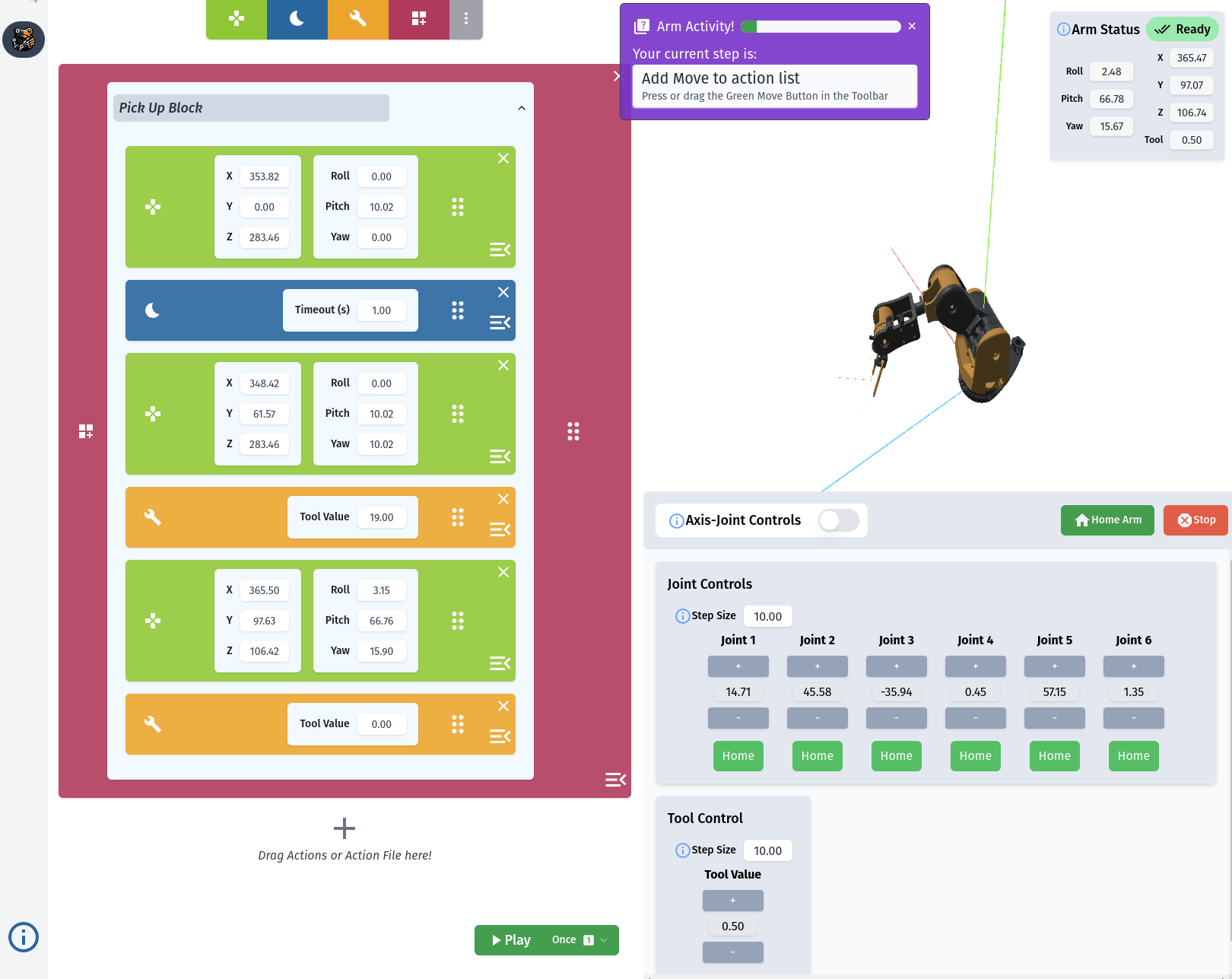
RiBot Controls
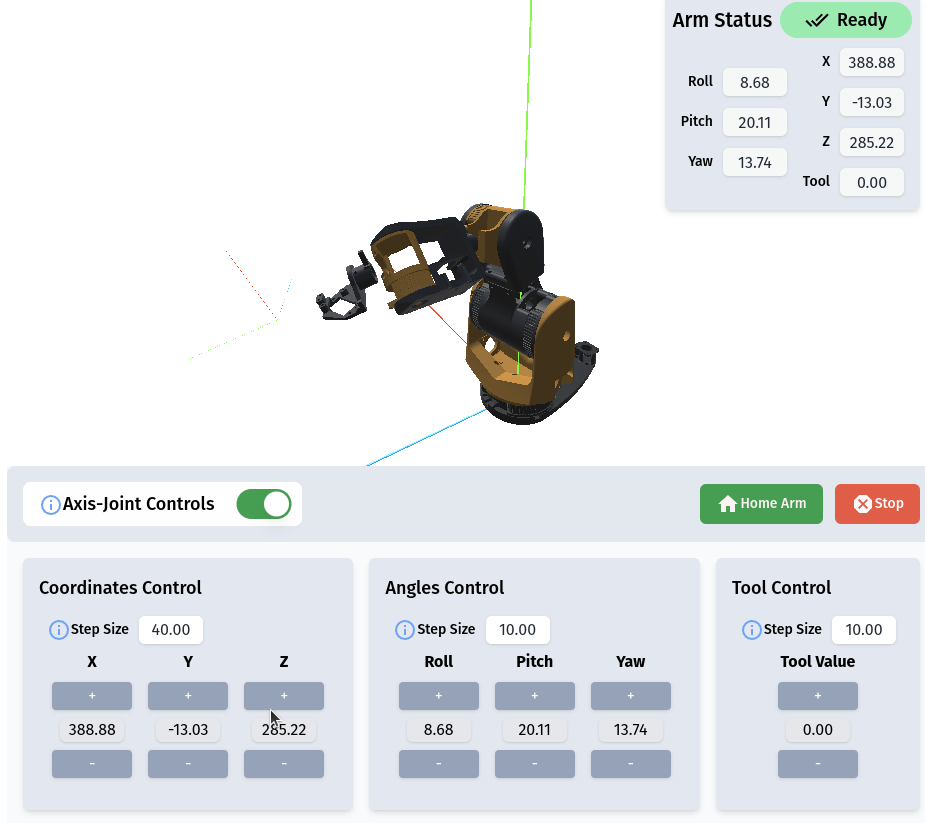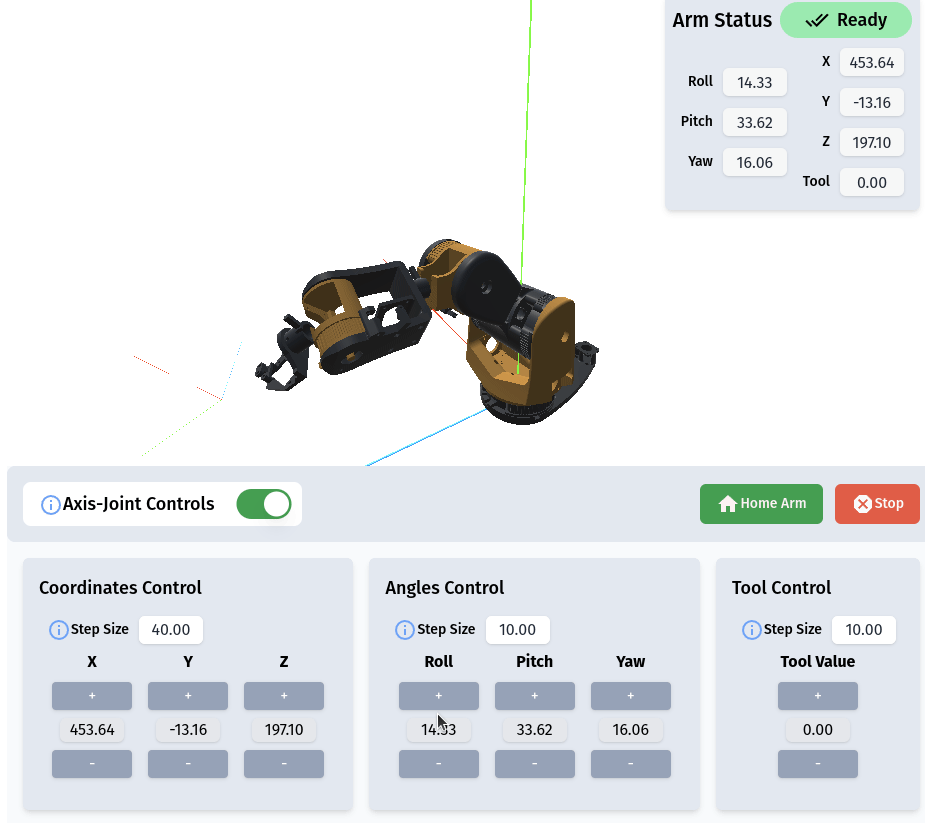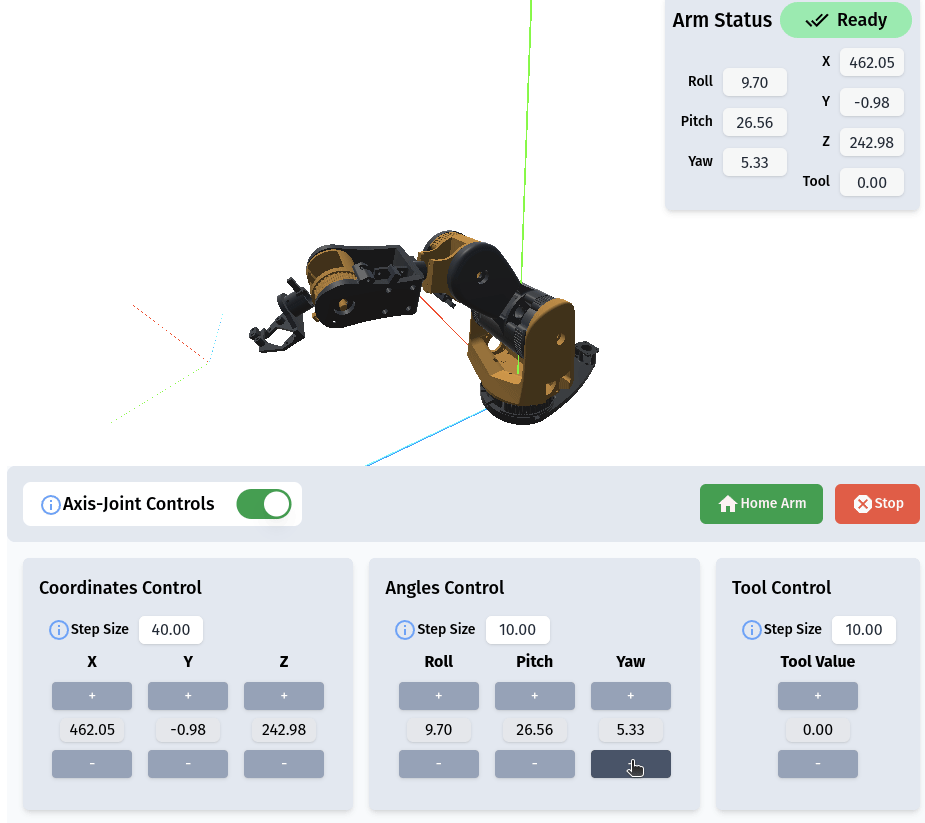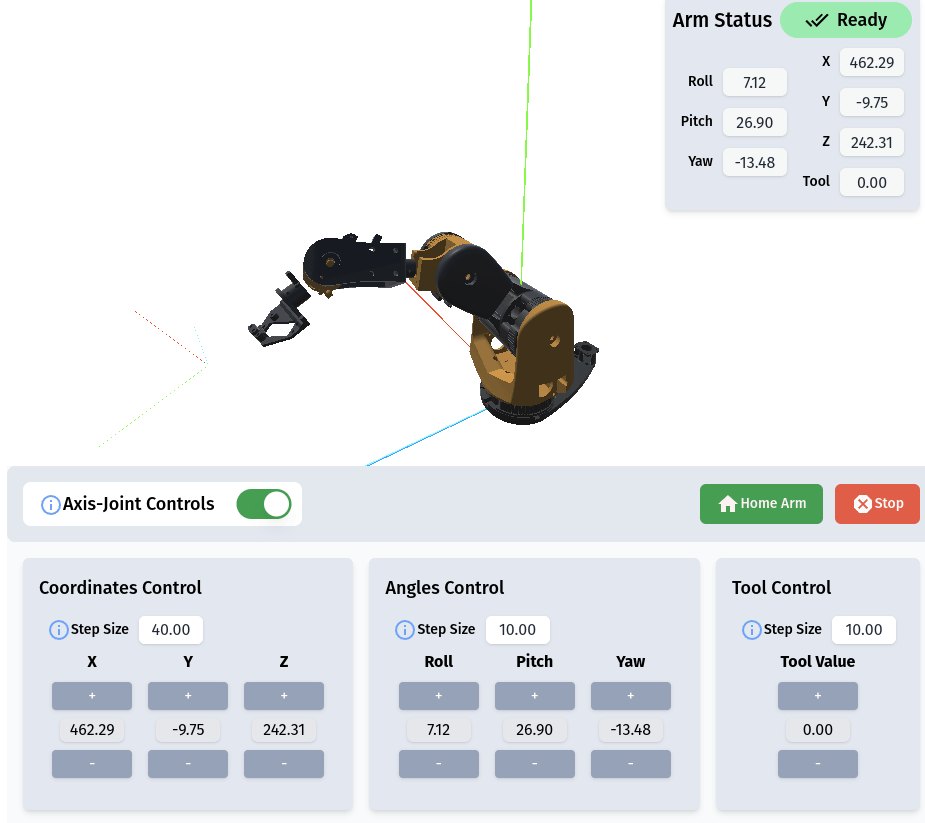
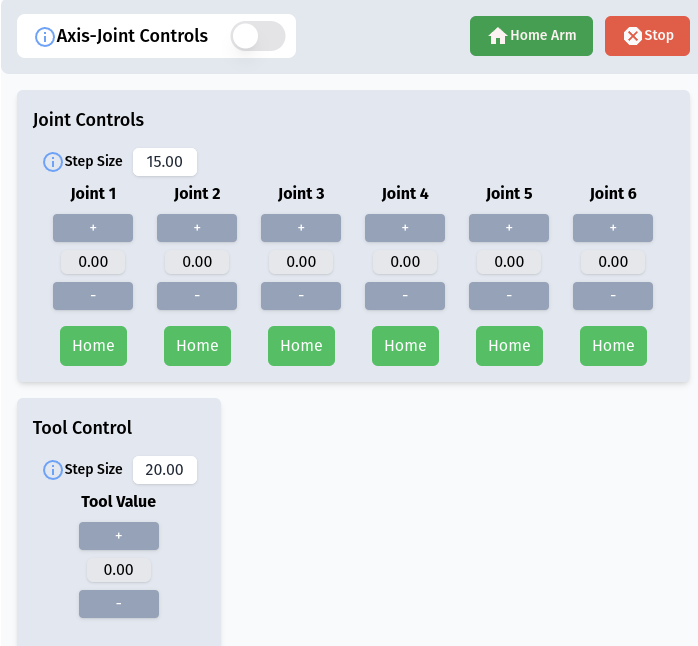
The Action List
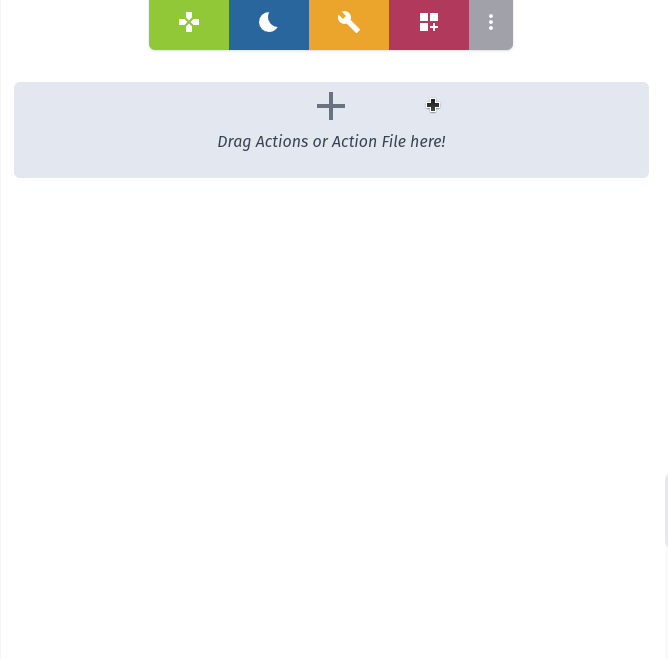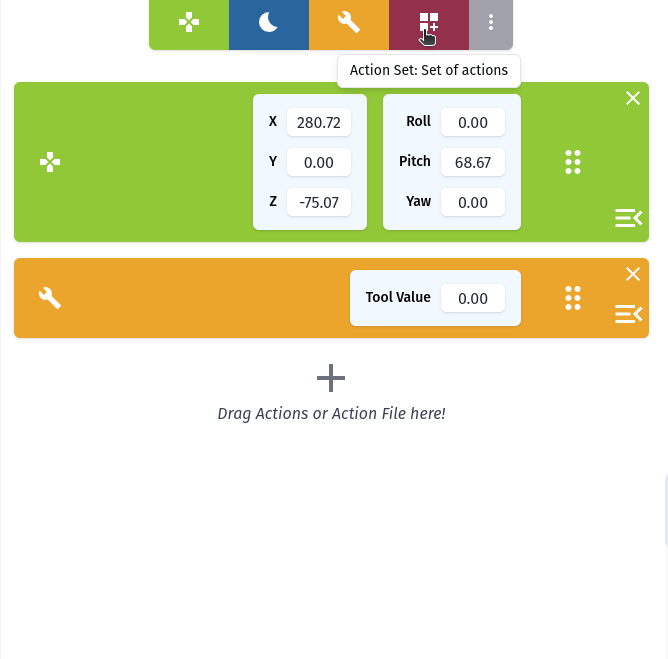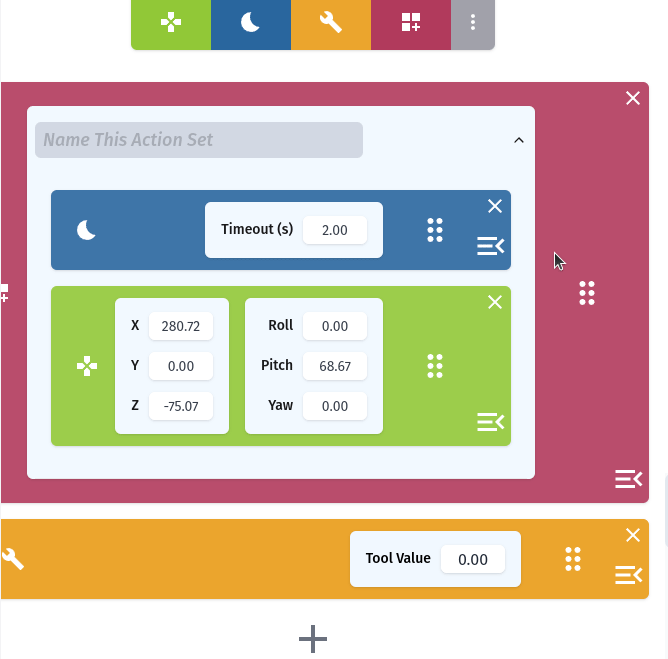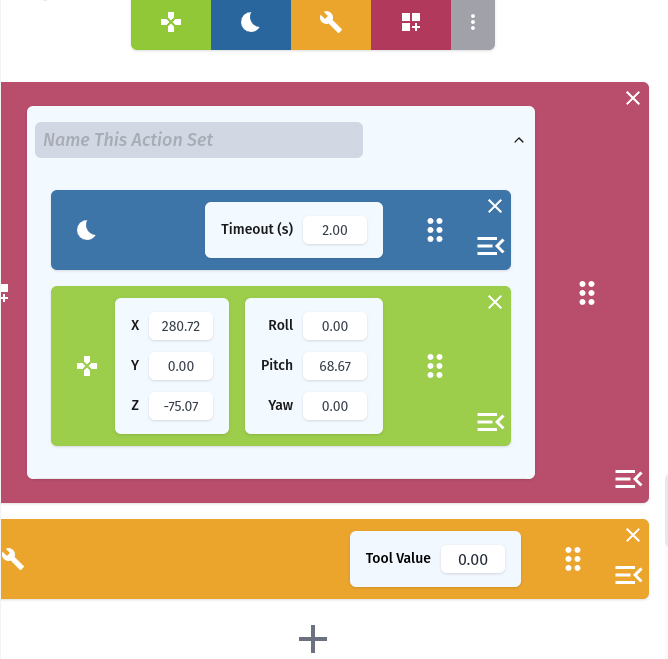
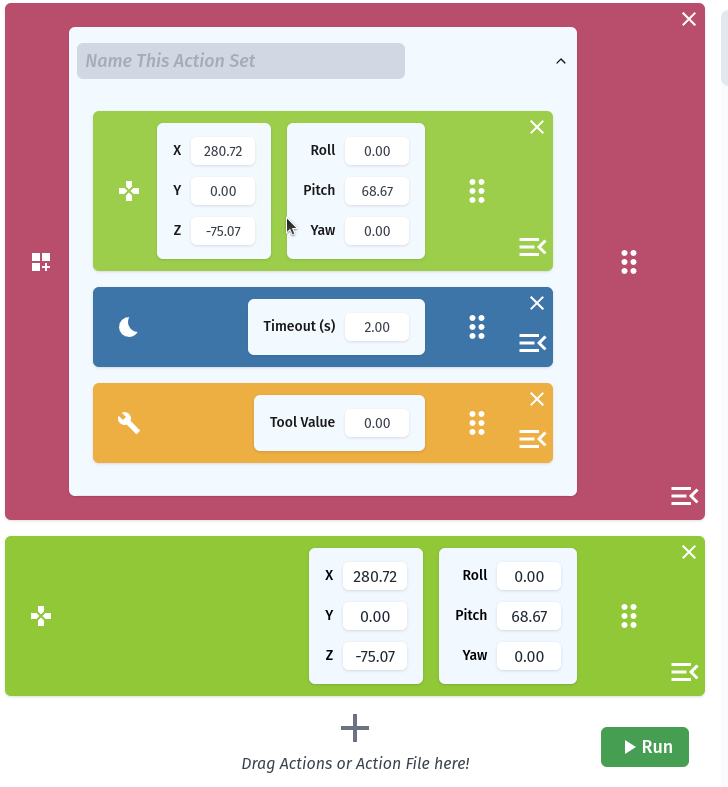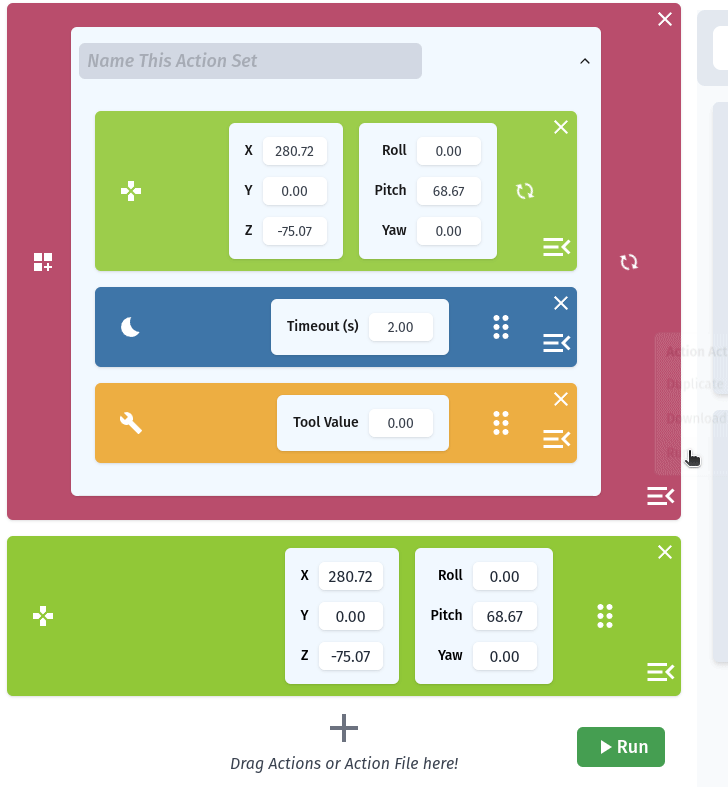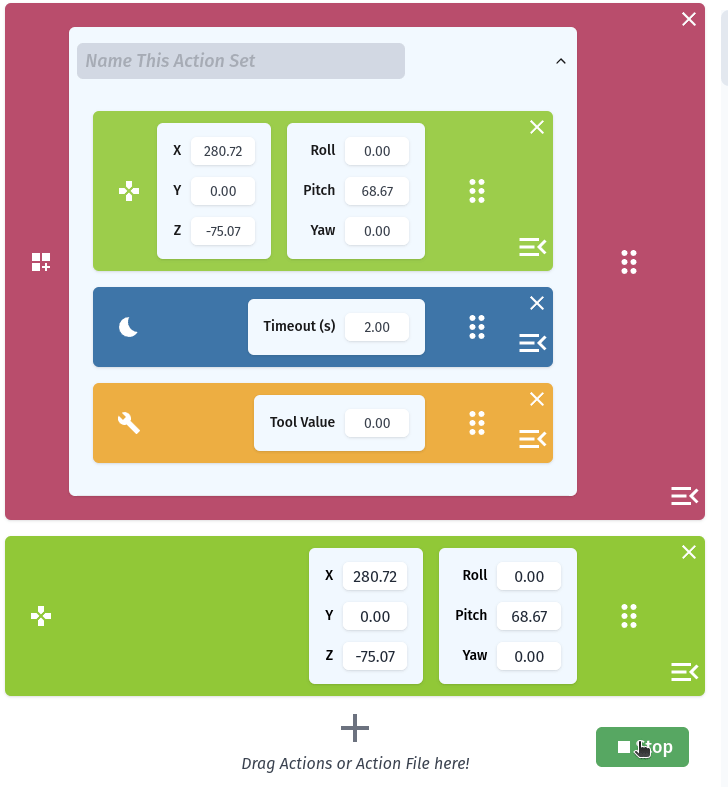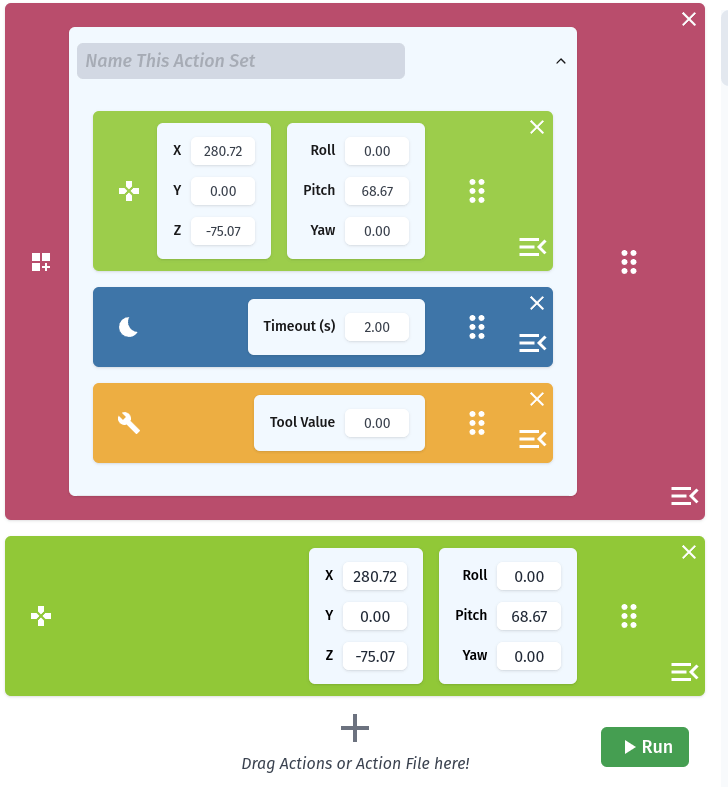
Requirements for Using RiBot
To utilize RiBot effectively, the following requirements are essential:
- A Compatible Robotic Arm: For our current implementation, the robotic arm must be operated using an ESP32 microcontroller.
- Six Degrees of Freedom: The system has been thoroughly tested and implemented on a robot arm with six degrees of freedom, ensuring a wide range of motion and versatility.
- Stepper Motors and Compatible Drivers: The tested arm uses stepper motors for each joint and StepStick stepper motor drivers. However, RiBot is compatible with any driver controllable via step and direction pins.
For more detailed information on the specific hardware used and implementation guidelines, please refer to the hardware section of our documentation.